Get Healthy!
Staying informed is also a great way to stay healthy. Keep up-to-date with all the latest health news here.
09 May
14 Types of Cancer Are on the Rise in People Under 50, Study Finds
Certain types of cancer are becoming increasingly common in people under 50, according to new research. These include breast, colon, kidney and uterine cancer.
08 May
Ultra-Processed Foods May Speed Up Early Signs of Parkinson’s Disease, Study Finds
In a new study, people who consumed the highest amounts of ultra-processed foods were more likely to show earlier signs of prodromal Parkinson’s disease, the stage of the disease seen before tremors begin.
07 May
Teen Use of Nicotine Pouches on the Rise
A new study finds more high schoolers are using nicotine pouches -- alone and in combination with e-cigarettes.
Sweet Tooth Explained: Researchers Reveal How We Taste Sugar
SUNDAY, May 11, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Why does sugar taste so good — and why do we want it so badly? Scientists may finally have the answer.
For the first time, researchers have figured out the structure of the sweet receptor — the tiny part of your tongue that tells your brain when something tastes sweet.
T...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 11, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Topical Antibiotic May One Day Treat Infected Ears
SATURDAY, May 10, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Any parent who has been jolted awake by the squeals of a toddler with an ear infection knows that relief won't be swift — or sure.
Kids often build resistance to the usual days-long antibiotic treatment regimen so the painful infections can come roaring back. But Cornell University rese...
- Carole Tanzer Miller HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 10, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Trump Taps Wellness Influencer Casey Means For Surgeon General
FRIDAY, May 9, 2025 (HealthDay News) — President Donald Trump has chosen Dr. Casey Means, a wellness influencer and health tech entrepreneur, to be his nominee for U.S. surgeon general.
The decision comes after Trump withdrew his previous nominee, Dr. Janette Nesheiwat, The Associated Press reported.
Trump ...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 9, 2025
- |
- Full Page
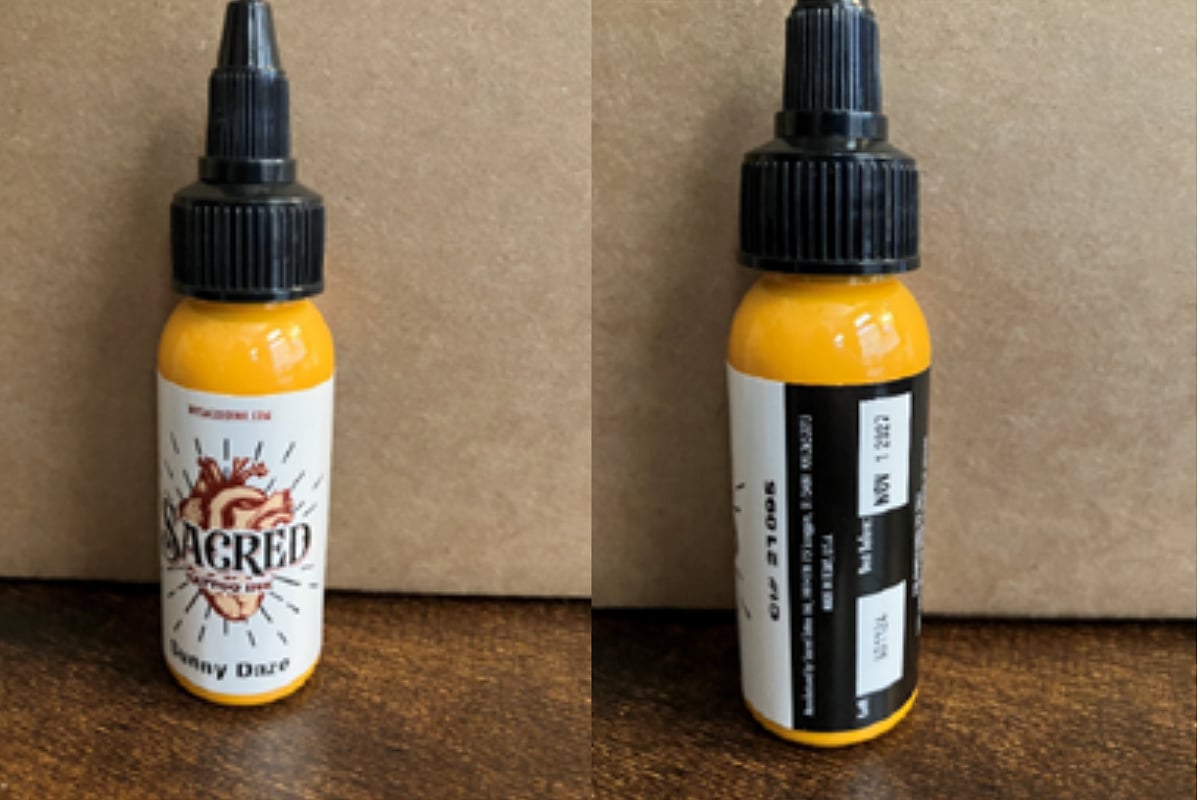
Thinking About a Tattoo? FDA Warns These Inks Could Be Dangerous
FRIDAY, May 9, 2025 (HealthDay News) — The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is warning consumers and tattoo artists that two tattoo inks have tested positive for harmful bacteria and could lead to serious infections.
The affected products are:
Sacred Tattoo Ink, Raven Black (CI# 77266; Lot#: RB0624, Best Before: ...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 9, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Some Cancers Increasing in People Under 50, New Report Shows
FRIDAY, May 9, 2025 (HealthDay News) — More young adults in the U.S. are being diagnosed with cancer, and researchers are trying to figure out why.
A new government report shows that rates of several types of cancer are going up in people under age 50, especially among women.
The study, led by scientists at the National C...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 9, 2025
- |
- Full Page
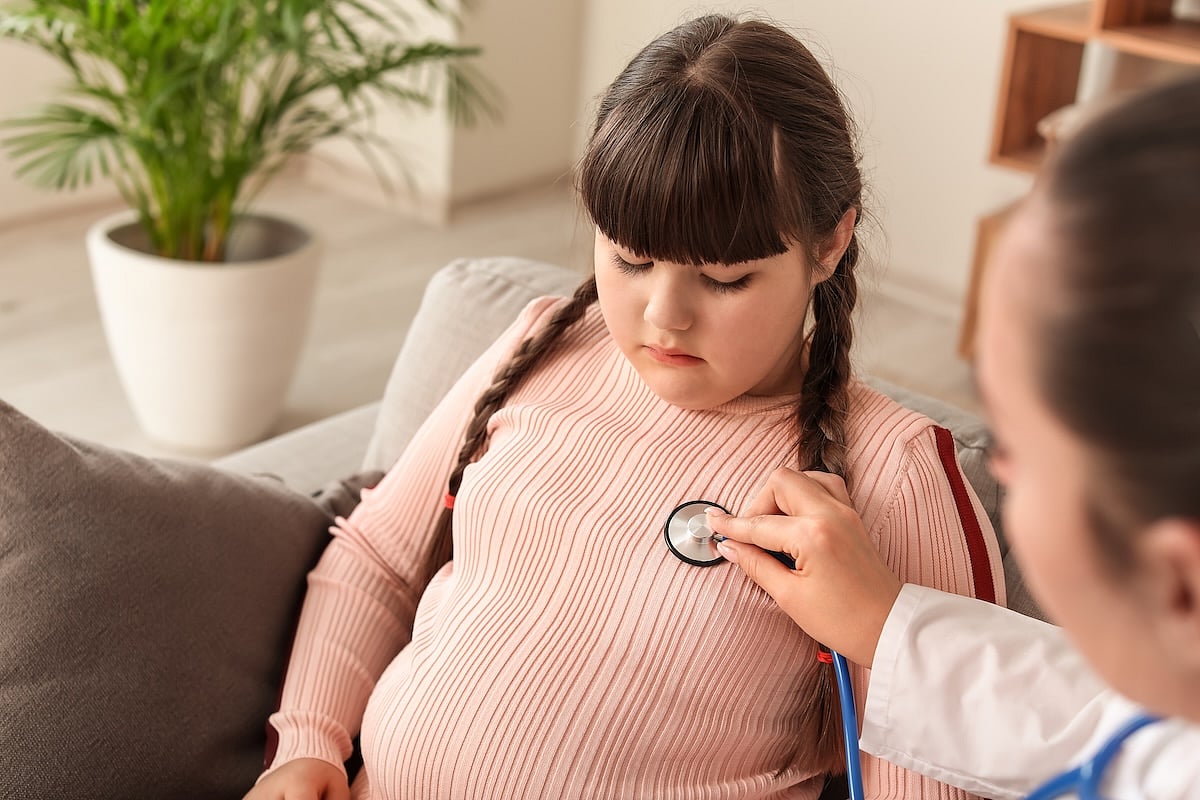
Childhood Obesity Triples Odds Of Weight Discrimination
FRIDAY, May 9, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Childhood obesity nearly triples a person’s risk for experiencing discrimination or stigma based on their weight, a new study says.
Severe obesity before age 18 increased a person’s odds of experiencing weight stigma by 2.8 times, researchers reported recently in the Internationa...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 9, 2025
- |
- Full Page
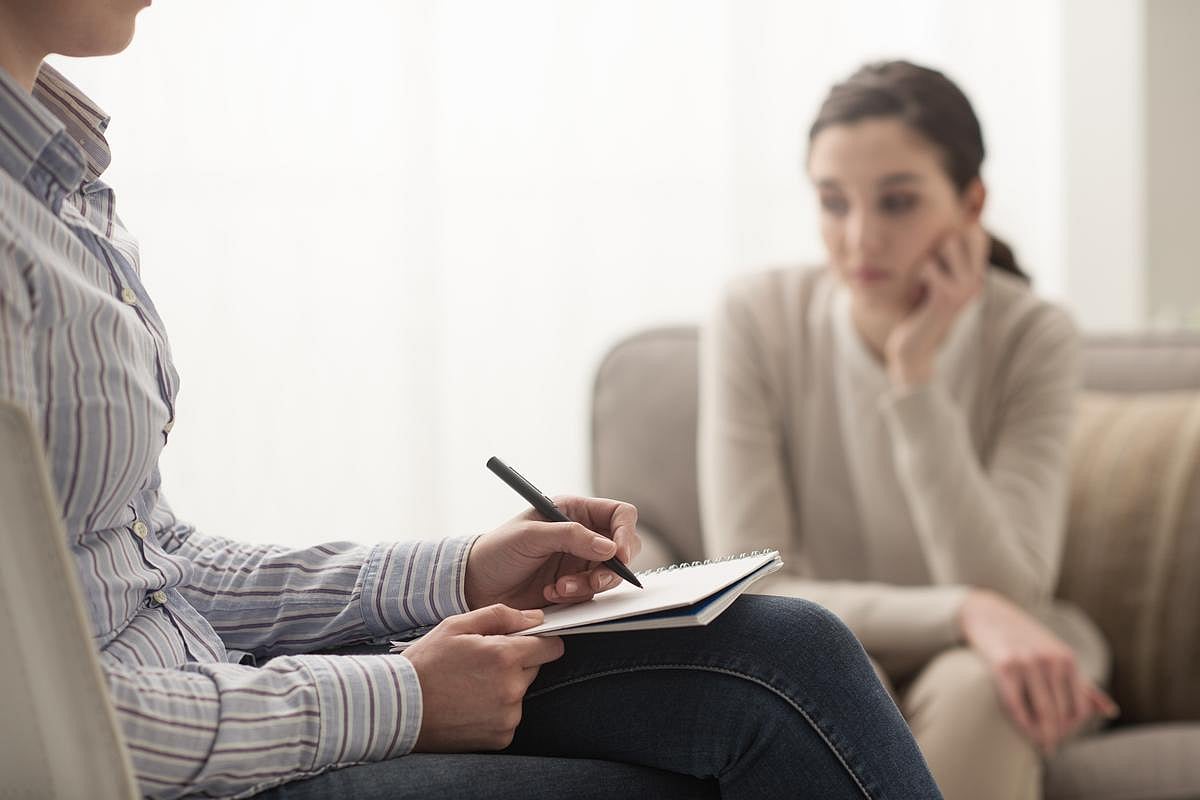
Talk Therapy On The Rise, Psychiatric Meds Used Less Often
FRIDAY, May 9, 2025 (HealthDay News) — More talk and fewer pills are being employed to help Americans maintain their mental health, a new study says.
Psychotherapy is assuming a larger role in mental health care, while medications prescribed without accompanying therapy are becoming less common, according to results published in earl...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 9, 2025
- |
- Full Page
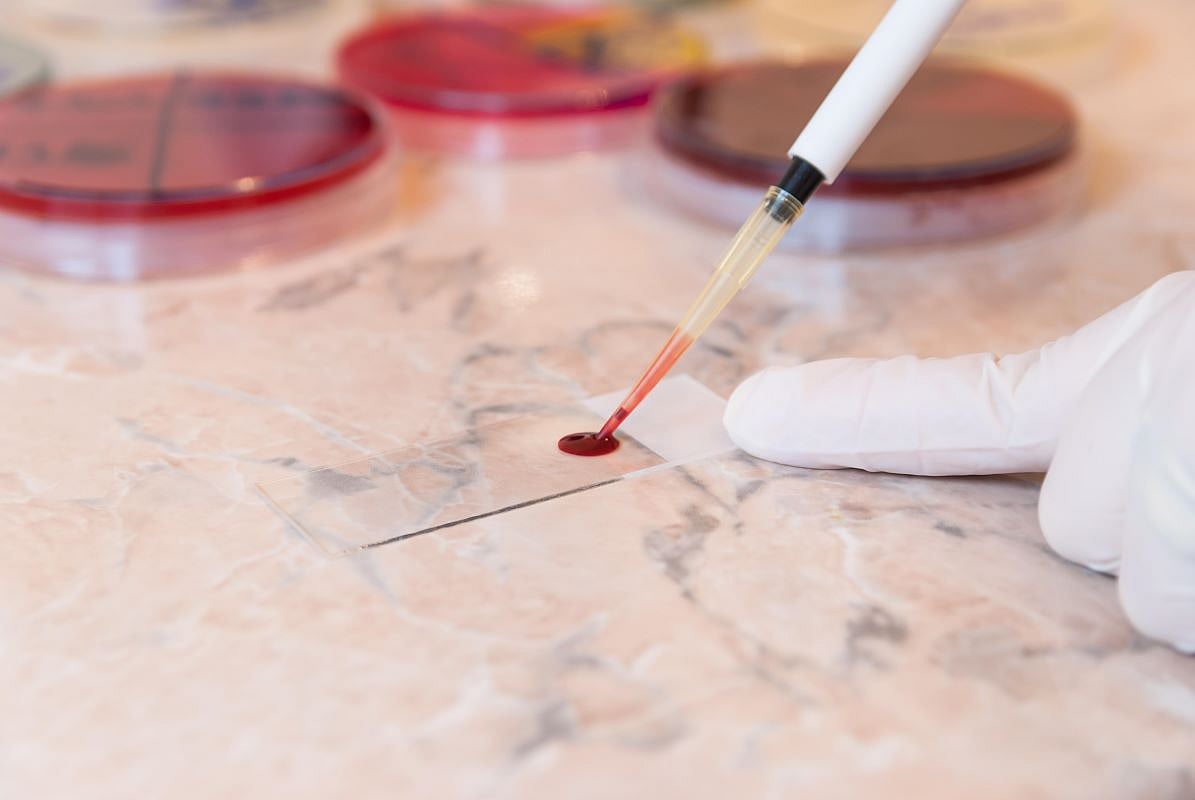
Blood Testing Could Catch Cancers Early, Projections Say
FRIDAY, May 9, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Blood tests could catch as many as half of cancers at an earlier, more treatable stage, a new study says.
If conducted every year or every other year, the multi-cancer early detection (MCED) blood test could help more people survive cancer, researchers reported May 8 in BMJ Open.
...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 9, 2025
- |
- Full Page
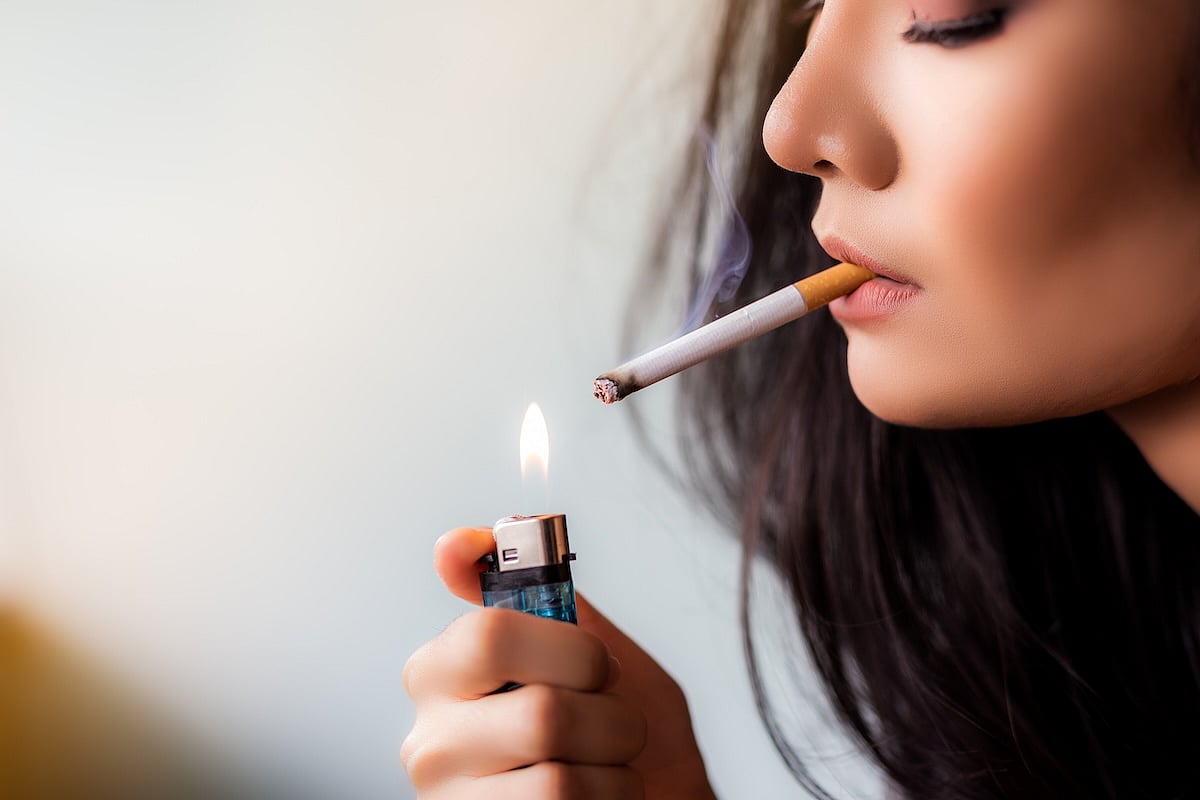
Smoking Doesn't Explain Increased COPD Risk For Women
Smoking can't explain why women are more at risk for COPD, a new study says.
Women are about 50% more likely than men to develop COPD even though they are less likely to smoke, researchers reported May 8 in the journal BMJ Open Respiratory Research.
Smoking tobacco is the main cause of COPD, the umbrella term for chronic bre...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 9, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Women With Autoimmune Disease At Greater Risk For Heart-Related Death
FRIDAY, May 9, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Women with common autoimmune inflammatory diseases are more likely than men to die from heart disease, a new study says.
Women with rheumatoid arthritis, lupus or systemic sclerosis have a 50% higher heart disease-related death rate than men, researchers reported May 5 in the journal Circula...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 9, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Ovary Removal Reduces Death, Cancer Risk Among Genetically Prone Breast Cancer Survivors
FRIDAY, May 9, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes appears to dramatically reduce the risk of death among breast cancer survivors who are genetically prone to cancer, a new study says.
Breast cancer survivors carrying BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene variants had a 48% overall lower risk of death after undergoing t...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 9, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Moderna's Combo Flu and COVID Shot Shows Promise
THURSDAY, May 8, 2025 (HealthDay News) — A new vaccine that combines flu and COVID-19 protection in one shot shows promising results, but the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) says it wants more data before it can be approved.
Moderna researchers reported that the combo shot produced a stronger immune response against COVID-19 ...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 8, 2025
- |
- Full Page
When Statins Aren't Enough, This Drug May Help Lower 'Bad' Cholesterol
THURSDAY, May 8, 2025 (HealthDay News) — A new drug combo lowers "bad" LDL cholesterol for people whose levels remain high even after taking statins.
The new pill pairs a new drug called obicetrapib with an existing one, ezetimibe. In a Phase 3 clinical trial, this combo reduced LDL levels by nearly 49% over about three months, accor...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 8, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Trump Administration Ends CDC's Key Infection Control Committee
THURSDAY, May 8, 2025 (HealthDay News) — A federal committee that helped set national rules for infection control in hospitals has been shut down, raising concerns from health experts.
The Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee (HICPAC) was terminated March 31, though members weren't told until early May, according...
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 8, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Face Mask Can Detect Kidney Disease Via Breath
THURSDAY, May 8, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Wearing a face mask to protect others from infectious disease continues to be hotly debated in the United States.
But what about wearing a face mask to detect chronic kidney disease?
A modified surgical face mask containing a specialized breath sensor can accurately detect when someone h...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 8, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Worried About Prostate Cancer Screening? New Study Shows Better Judgment In Treatment
Some men would rather skip screening for prostate cancer due to fears that they’ll be rendered impotent or incontinent from cancer surgery.
But new research says those fears are unwarranted, thanks to improvements in the way doctors approach prostate cancer.
The number of unnecessary surgeries to treat low-risk prostate cancer ...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 8, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Down Syndrome Patients Have Higher Stroke, Heart Attack Risk
People with Down syndrome have a much higher risk of stroke than people without the genetic disorder, a new study says.
Down syndrome patients have a 5.14 times higher risk of a stroke caused by a brain bleed, and more than 4 times higher risk of a stroke caused by a blood clot, researchers reported May 7 in the Journal of Internal Med...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 8, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Early Alzheimer's Testing Can Provide Peace Of Mind
THURSDAY, May 8, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Knowing your risk for Alzheimer’s disease can provide peace of mind, but also might contribute to complacency regarding your overall health, a new study says.
People who underwent brain scans to learn their Alzheimer’s risk experienced less anxiety, even if the results showed highe...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 8, 2025
- |
- Full Page
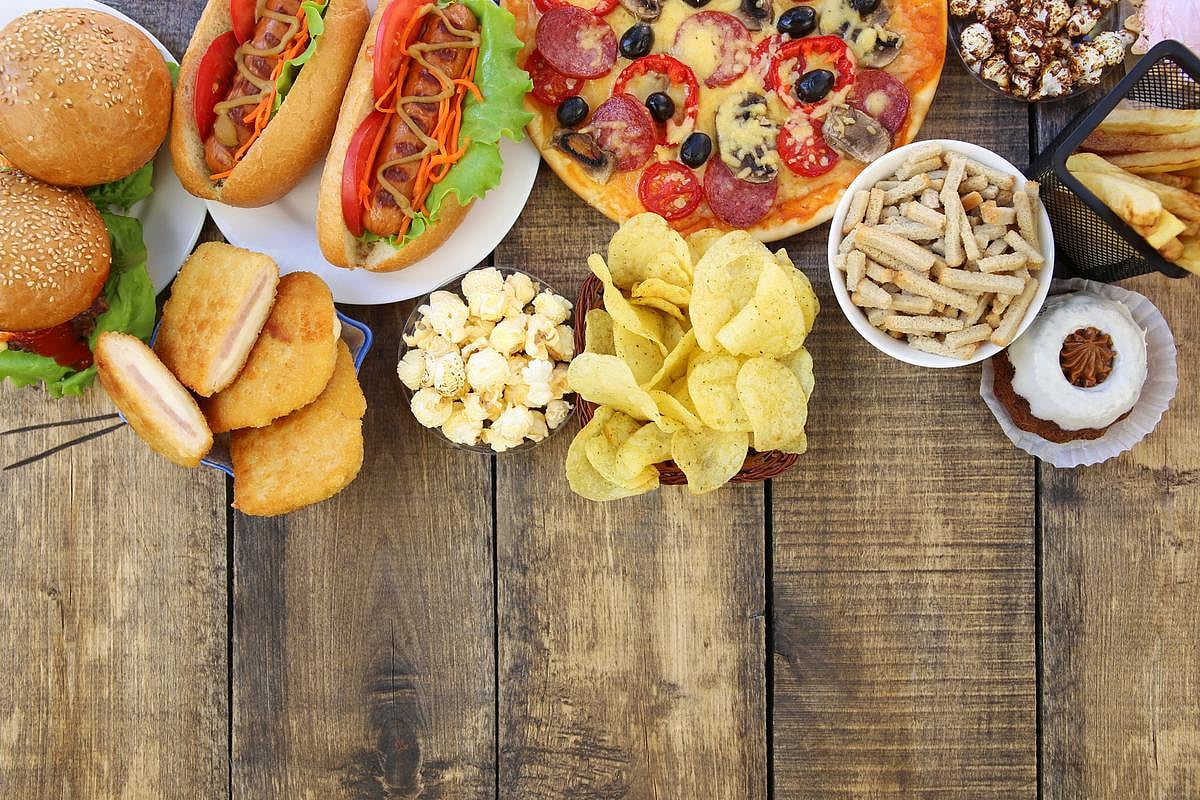
Ultra-Processed Foods Linked To Parkinson's Disease Risk
Fast food and ready-made packaged eats could be doing slow damage to people’s brains.
Ultra-processed foods like breakfast cereals, soft drinks, hot dogs and ketchup appear to increase a person’s risk of developing Parkinson’s disease, a new study says.
People who ate about 11 servings of ultra-processed foods per d...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 8, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Sleep Apnea Linked To Memory-Related Brain Decline
Sleep apnea could be costing you brain power and increasing your risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, a new study says.
The drop in blood oxygen levels that occurs during a sleep apnea episode appears to be linked to degeneration of brain regions associated with memory, researchers reported May 7 in the journal Neurology
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- May 8, 2025
- |
- Full Page